There are different types of CMS: Shopify, Prestashop, WordPress, Drupal ... Choose the one that best suits your needs.
Contents
What is Drupal?
Drupal is a free open-source content management system (CMS). With several million users worldwide, it is one of the most popular CMS. Many website owners, amateurs and professionals alike, use it to create and administer their websites with ease. You probably use Drupal every day without knowing it. Drupal is published under the GNU public license, which means that it has significant advantages in terms of cost, flexibility and security. It can be modified freely by people with some knowledge of development. It is therefore free of any lock-in and offers a complete view of the site's source code.

Many features and infinite customization
Drupal is a reference in CMS. It provides an intuitive user interface that makes it easy to edit and publish content. The platform offers great flexibility and is capable of supporting an unlimited number of content of all types: text, videos, images, forms ... It retrieves content from the back office to present it dynamically on the front office. Drupal offers a content classification system and a rights management system to allow you to have total control over your content.
Drupal's functionality comes from modules (also called plugins) that can be downloaded from Drupal.org. What you download from Drupal.org is called the "Drupal core". It comes standard with all the most commonly used modules, but there are also many modules released for free by independent developers.
Drupal, at the cutting edge of technology
Drupal is also a powerful development platform that adheres to modern programming models. It allows the use of PHP best practices and HTML5 and YAML. Drupal integrates technologies such as CKEditor, Symfony2, Twig, jQuery, Backbone.js, and Guzzle among others.
How does Drupal work?
After completing the installation process, you will automatically land on a login page for your CMS. Once connected, you will see different links that lead to different parts of the site. Here is what they contain:
- Content - In this part you can create content, articles or static pages. This is also the place where you can moderate comments and where you can find your image library.
- Structure - This is where you can manage all the structural elements of your site, such as forms, blocks, menus and taxonomies.
- Appearance - This is where you can change the theme settings and other appearance-related plugins. You will also find the different updates of your theme.
- Extensions - Here you can install and uninstall various Drupal modules.
- Configuration - This is an access to the general and default settings of your site.
- Users - Here you can manage the different rights and permissions for each user.
- Reports - This is where you get reports about updates, errors and site status.
- Help - This is a help center where you can find useful information about the basic administration of the site as well as about the modules installed on your site.
Changing your Drupal site’s theme
The default Drupal theme is of course only an example. It is up to you to change the appearance of your site by changing the default theme. You will find an option to do so under Appearance > Install a new theme.
However, unlike other CMS like WordPress, it is not possible to find themes inside the Drupal backend. You have to go to the official Drupal themes directory, whose link is indicated at the top of the theme installation page. There are now, in 2019, just under 3,000 themes, which you can of course filter according to your needs.
When you choose a theme, you have to make sure that it corresponds to your level of technical skills and that it allows you to create the site you have in mind. To help you, all the themes in the directory have their own dedicated page, where you will find a live demo. Once you have selected your theme, its installation is relatively easy. Just download the theme from the directory (you'll find options at the bottom of the page) or right-click on the download link to copy its location.
Then you can use the file or URL to upload the theme to your site. All that's left is to install it from the Appearance tab and activate it.
Create a home page
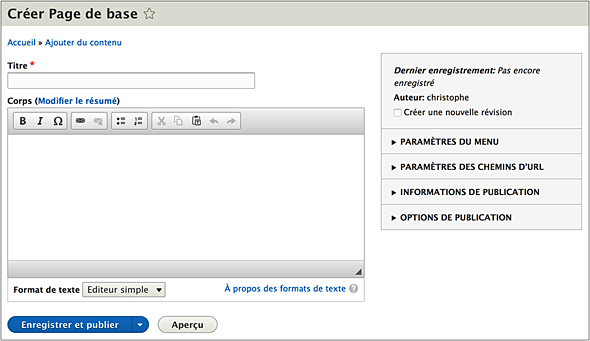
Now that your site has a custom design, it's time to fill it in! First, start by creating a homepage, by first creating a page via the content tab > Add Content > Base Page. This will take you to the Drupal page editor.
Below it, you will find an "Edit Summary" link. When you click on it, you can write a summary for your article or static page. This is a kind of excerpt that will appear on some categories of your site. Just below, you can enter your text and format it. You can use WYSIWYG or use the HTML editor. Some additional options such as entering tables or horizontal separators are indeed available when you switch to full HTML at the bottom.
Once you have finished writing and formatting your content, you need to set the URL slug (located under the URL alias). The choice of the slug should not be done randomly because it is important for SEO.
Your page is now registered and published. To create your homepage, you must now go to Configuration > System > Basic Site Settings. Here, under Default Home Page, enter the same URL you just defined for your new page. This manipulation allows you to display a static page and not your articles in chronological order.
Create a menu
The menu is an essential setting for any site. To add a page to a menu, you just have to create it and make sure, before publishing it, to check the box "Provide a menu link".
Here is how to fill in the parameters that appear:
- Menu Link Title = the link text that users will see in the navigation menu.
- Description: will appear when the user hovers over the menu link. This is an option that can be skipped.
- Parent Item: If your menu already has a level, you can create sub-categories here.
- Weight: Here you determine the order of your menu items. The higher the number, the higher the item will be ranked.
Enable and disable default modules
Drupal comes with a set of modules that you can find under "Extensions". These will not necessarily be installed and active by default. If you want to use them, just check the corresponding box and click on Install. The CMS will take care of the rest. In the same way, modules that you do not need can be removed by clicking on "uninstall".
How to optimize Drupal for SEO?
Like many CMS, Drupal is not totally SEO Friendly in its basic version. Here are several modules and tips for this.
Download Drupal SEO Checklist
This module is actually a smart checklist of modules you will need for SEO.
By following the Drupal SEO listyou can implement the best modules needed to optimize your website. The module tasks are segmented according to functional requirements such as title tags, paths, content and more. Each task provides a download link for the module in question. Beware, the SEO Checklist module tells you what to do, but it does not tell you how to do it. So you need to read up on SEO best practices.
Clean up URLs with the Redirect module
For effective optimization, you need to ensure that your URLs are clean, that your site displays the right content, and that your internal linking is maintained even when your content changes. One way to do this is through 301 redirection 301. With the Redirect module, you'll be able to redirect old, obsolete URLs and even fix broken links.
Implement meta tags
Meta tags are essential in the optimization of Drupal 8. They are snippets of text read by search engines. They improve your SEO by clearly communicating the content of your pages. The Metatag module is very useful in this case. It automatically places both the HTML title tag and the meta tags in the header of a web page.
Communicate directly with search engines through the sitemap
The XML Sitemap module creates an XML sitemap of your content that you can submit to search engines. An XML sitemap is simply a map of your site, formatted to be understood by robots. Submitting an XML sitemap helps your SEO by giving Google a list of all the pages that you want to be crawled. The more complex your site is, the more recommended this sitemap is.
Conclusion
Drupal is a powerful CMS and a great way to create your own website. It has all the necessary features for simple or complex websites. Flexible and free, Drupal is nevertheless a quality CMS that uses the latest web technologies. It is therefore the guarantee of an up-to-date site, in terms of accessibility but also security.